Fast + Comprehensive: Two Molecular Technologies
The qPCR + NGS solution
MicroGenDX qPCR+ NGS offers you two detailed diagnostic reports in rapid succession.
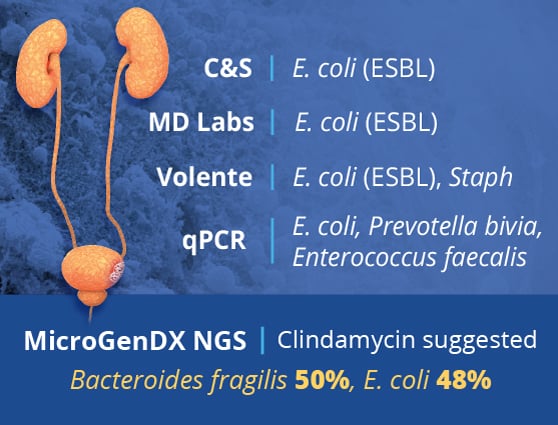
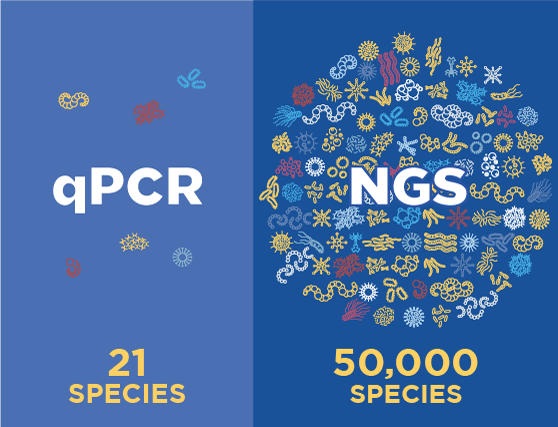
The first, a qPCR report in 24-48 hours, provides total bacterial load, any antimicrobial resistance genes present, and detection of a few known pathogens. Physicians find the antimicrobial resistance genes helpful for patients who are already on antimicrobial treatment. However, qPCR will only detect the commonly-known microbes selected for a limited qPCR panel. Because of this, qPCR by itself can miss the dominant species in the sample up to 60% of the time. Which means that initiation of new antimicrobials is not recommended prior to receiving the NGS report that follows.
The second report provides next-generation sequencing (NGS) results in 3.5 days. This includes everything in the qPCR report, plus a complete list of clinically relevant microbes in the sample — and their abundance distribution — using NGS. These microbes are referenced against a custom database of over 50,000 species. In addition, the qPCR+NGS report offers research-based antimicrobials for consideration, based on the Sanford Guide and Johns Hopkins Guides. These combined qPCR+NGS results provide detailed and accurate clinical diagnostic information for the most confident treatment decisions.
| qPCR | NGS | |
|---|---|---|
| Results in | 24-48 hours | 3.5 days |
| Information provided |
|
|
| Treatment considerations |
|
|
References
- Matthew Dixon, Maria Stefil, Michael McDonald, Truls Erik Bjerklund-Johansen , Kurt Naber, Florian Wagenlehner, Vladimir Mouraviev. Metagenomics in diagnosis and improved targeted treatment of UTI. World J Urol . 2020 Jan;38(1):35-43. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02731-9.
- Internal competitive analysis of qPCR and NGS – data on file.