The Best Diagnostic Tools for Orthopedic Infection Patients
MicroGenDX OrthoKEY® offers the ideal synergy of evidence-based diagnostics for periprosthetic joint infection
MicroGenDX OrthoKEY PJI OR and OrthoKEY PJI Clinic offer you the essential diagnostic compliment to culture that combines biomarkers for infection with molecular analysis – at the lowest cost and fastest turnaround on the market.
In contrast to what actually grows in culture, next-generation sequencing (NGS) identifies both the growth potential of clinically relevant microbes in a sample, and the relative abundance of those microbes. NGS analysis was recommended by a 2018 International Consensus Meeting strong consensus for identifying culture-negative infections — which NGS identifies 80-90% of the time.
MicroGenDX’s NGS protocol includes both positive and negative controls. Positive controls consist of known species and predictable results that can be verified in each stage of the process — ensuring each stage is performed correctly. The negative control consists of sterile water, run as a parallel sample to confirm that no contamination has occurred during any stage of the process.
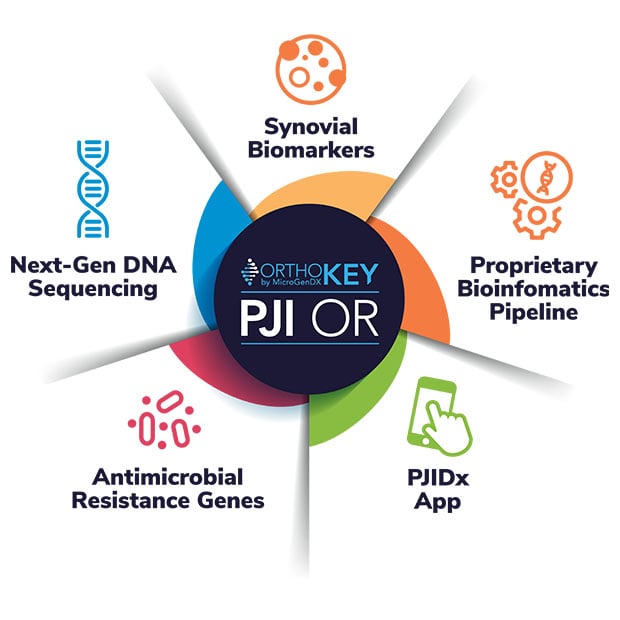
OrthoKEY PJI OR, peace of mind for revision procedures, includes:
- Synovial biomarkers (CRP, WBC, PMN%) and antimicrobial resistance genes in 24-48 hours
- NGS identification of microbes from synovial fluid, implant wipe-downs, and swabs in 3.5 days.
- PJIDx diagnostic app — a guideline-based, AI-driven app provides probability of infection based on combined NGS and biomarker results
OrthoKEY PJI Clinic, taking the mystery out of in-clinic PJI diagnostics, includes:
- Synovial biomarkers (CRP, WBC, PMN%) and antimicrobial resistance genes from aspiration sample in 24-48 hours
- NGS identification of microbes from synovial fluid in 3.5 days
- PJIDx diagnostic app
Total joint arthroplasty failure predicted by NGS in landmark prospective multicenter study
In 2020 a prospective multicenter study demonstrated that 68.6% of revision failures following two-stage exchange were due to untreated or undertreated pathogens that were missed by culture, but detected by NGS at the time of initial resection. Read about study
References
- Corona P S, et al. General Assembly, Diagnosis, Pathogen Isolation: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. The Journal of Arthroplasty. 34 (2019) S207eS214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2018.09.072
- Ivy MI, Sharma K, Greenwood-Quaintance KE, Tande AJ, et al. Synovial fluid alpha defensin has comparable accuracy to synovial fluid white blood cell count and polymorphonuclear percentage for periprosthetic joint infection diagnosis. Bone Joint J 2021;103-B(6):1119–1126. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.103B6.BJJ-2020-1741.R1

 Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic Joint Infection Non-union Trauma
Non-union Trauma