Fast + Comprehensive: Two Molecular Technologies
The qPCR + NGS solution
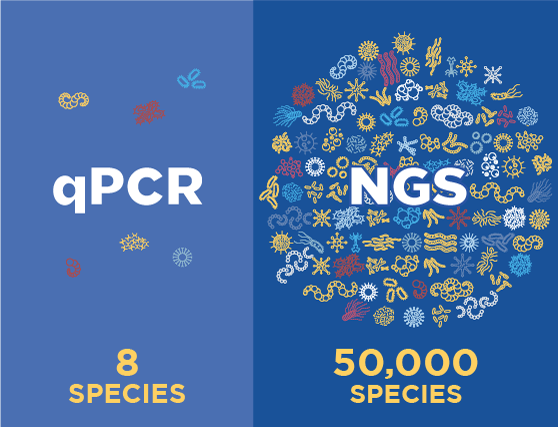
MicroGenDX offers you two detailed molecular diagnostic reports in rapid succession.
The first, a qPCR report in 24-48 hours, provides total bacterial load, any antimicrobial resistance genes present, and detection of a few known pathogens. Physicians find the antimicrobial resistance genes helpful for patients who are already on antimicrobial treatment. However, qPCR will only detect the commonly-known microbes selected for a limited qPCR panel. Because of this, qPCR by itself can miss the dominant species in the sample up to 60% of the time. Which means that initiation of new antimicrobials is not recommended prior to receiving the NGS report that follows.
The second report provides next-generation sequencing (NGS) results in 3.5 days. This includes everything in the qPCR report, plus a complete list of clinically relevant microbes in the sample — and their abundance distribution — using NGS. These microbes are referenced against a custom database of 57,000 species. In addition, the qPCR+NGS report offers research-based antimicrobials for consideration, based on the Sanford Guide and Johns Hopkins Guides. These combined qPCR+NGS results provide detailed and accurate clinical diagnostic information for the most confident treatment decisions.
Consensus guidelines: NGS recommended within first four days
2017 expert panel consensus guidelines determined DNA sequencing plays an essential role in the identification and treatment of chronic nonhealing wounds, and recommend initiating DNA identification of microorganisms in first four days of treatment.
| Days 1-4 | Days 5-7 | 1-4 Weeks | Continue until healed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiate multiple combined therapies including DNA identification of microbes | Optimize/personalize therapies according to healing status | De-escalate treatment as wound improves | Standard care OR Step up to advanced therapies |
The power of NGS over culture alone
| C&S Positive Results | 168 Chronic Wound Infection Samples | NGS Positive Results |
|---|---|---|
| 41 | Staphylococcus aureus | 72 |
| 2 | Streptococcus spp. | 41 |
| 20 | Staphylococcus spp. (not S. aureus) | 47 |
In a published retrospective study of 168 chronic wound patients, the majority of bacteria identified by molecular testing were not identified with culture. Although 17 bacterial taxa were identified with culture, 338 bacterial taxa were identified using DNA sequencing.
MicroGenDX combined qPCR+NGS provides you the most comprehensive picture of the microbial community in the wound bed – including polymicrobial biofilms – to empower you with the most targeted and effective therapeutic options.
References
- Schultz G, Bjarnsholt T et al. for the Global Wound Biofilm Expert Panel. Consensus guidelines for the identification and treatment of biofilms in chronic nonhealing wounds. Wound Rep Reg. 2017;25, 744–757. VC 2017 by the Wound Healing Society.
- Rhoads D, Wolcott R et al. Comparison of Culture and Molecular Identification of Bacteria in Chronic Wounds. Int J Mol Sci. 2012; 13(3): 2535–2550. doi: 3390/ijms13032535
