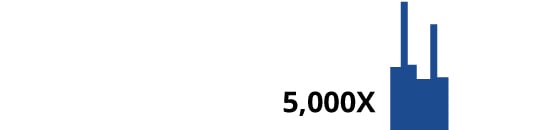qPCR + Targeted 16S/ITS NGS Diagnostic Technology
DNA detection with the greatest clinical utility
MicroGenDX combines qPCR with targeted 16S/ITS NGS to deliver timely, highly accurate, actionable diagnostic information for infections. Matching samples against a curated database of over 57,000 microbial species, MicroGenDX’s qPCR+NGS results identify all potentially pathogenic microbial taxa, along with their clinically relevant distribution in the sample, in 3.5 days, at a low cost. In contrast, the strain-level resolution and discovery power of shotgun metagenomics does not provide any greater diagnostic utility for most infections* — and shotgun is also slower and more expensive, with lower sensitivity and accuracy than targeted NGS. For clinical applications, qPCR and targeted NGS offer a clear advantage for optimal treatment strategies.
Comparison of DNA sequencing technologies
| qPCR | Targeted 16S/ITS NGS | Shotgun Metagenomics** | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overview |
|
|
|
| Strengths |
|
|
|
| Llimitations |
|
|
Sequence library is much smaller |
*Shotgun metagenomics may discover additional resistance genes, but MicroGenDX qPCR detects a total of 17 resistance genes from among all main classes of antimicrobials.
**MicroGenDX is also able to provide shotgun metagenomics offered by its RTL Genomics research division.References
- Mitchell SL, Simner PJ. Next-Generation Sequencing in Clinical Microbiology: Are We There Yet? Clin Lab Med. 2019 Sep;39(3):405-418.doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2019.05.003.
- https://www.illumina.com/content/dam/illumina-marketing/documents/gated/10143_Shotgun_Metagenomics_Methods_Guide.pdf