- European Urology Supplements Volume 16, Issue 10, November 2017, Page e2656 Meeting Abstract: The introduction of next generation sequencing (NGS) via DNA technology allows us to analyze the complete genomic profile of the gut microbiota with detection of resistance genes to the most frequently used antibiotics in empiric prophylaxis. The aim of our study was to evaluate NGS of rectal swabs prior to transrectal prostate biopsy to prevent infectious complications. Read Abstract…
- AUA News VOLUME 23 | ISSUE 7 Article: The discussion regarding the best strategies for selecting prophylaxis for prostate biopsies to minimize infectious complications continued in this year’s sessions. One group reported on the use of next generation DNA sequencing to test rectal swabs for the purpose of tailoring the prebiopsy antibiotic regimen (MP15-14). Infectious complications were avoided in 23 of 24 patients, with only a single patient having cystitis 3 weeks after biopsy.
- University of CO 2019 ABSTRACT: Pathogenic microorganisms could be responsible for asymptomatic and symptomatic inflammatory processes in the prostate including Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas spp., Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Trichomonas vaginalis, etc (1). Modifications of bacterial populations were observed according to different inflammatory and tumor conditions in prostate cancer (PCa) samples, which may promote the development of cancer by enhancing extracellular environmental factors within the prostate (2-4). Most of these studies have used polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques to identify specific microorganisms. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has much higher sensitivity than PCR to identify microorganisms in biological samples. We investigated microorganisms in post-digital rectal […]
- Rev Urol. 2017;19(4):213–220. STUDY: 44 acute cystitis patients and 22 control group patients were treated based on either C&S or qPCR + NGS DNA sequencing results. The acute cystitis patients and the control group patients were randomly assigned to be treated either based on culture results or qPCR + NGS DNA sequencing results. On day 14, symptom scores from those treated based on qPCR + NGS DNA sequencing results were statistically better than for those treated based on culture results.
- Can J Urol. 2018;25(3):9349-9356. STUDY: qPCR + NGS was used to identify bacterial and fungal pathogens in 112 UTI patients (acute cystitis, rectal swabs before transrectal prostate biopsy, neurogenic bladder, and chronic bacterial prostatitis). In comparison to culture analysis, qPCR + NGS patients experienced superior targeted treatment outcomes related to detection of resistance genes and anaerobic and culture-independent pathogens. Read Study…
- The Journal of Urology. 2018;199(4S): e283. Supplement, Friday, May 18, 2018. Meeting Abstract: In a retrospective study, urine-derived nucleic acid samples were assessed using qPCR + NGS to monitor 13 neurogenic bladder patients. All 13 patients had between 1 and 9 microorganisms present, 10 with a high bacterial load and one with 5 fungal species. Nine patients had antibiotic resistance genes, with 6 having multidrug resistance. Significantly, quinolone resistant E.coli was present in many of the patients, suggesting a required change from empiric therapy to a tailored treatment protocol. Read Abstract…
- The Journal of Urology. 2018;199(4S):e194. Supplement, Friday, May 18, 2018. Meeting Abstract: In a phase I study, rectal swabs from 24 patients were collected prior to transrectal prostate biopsy. Based on qPCR + NGS nucleic acid analysis, clinicians provided an individualized, targeted prophylaxis in 15 patients with multidrug resistance (14 patients with fluoroquinolone resistance). In 8 patients, different fungal species were detected, with multi-fungal associations in 4 of these. Subsequent targeted prophylaxis prevented infectious complications in 23 of the 24 patients. Read Abstract…
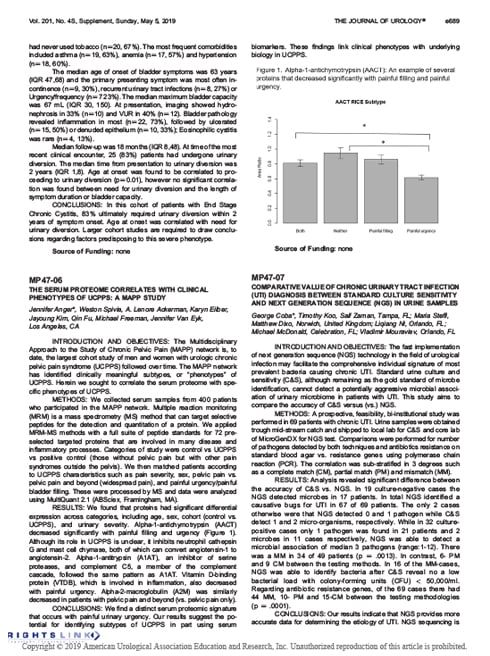
- The Journal of Urology. 2019;201(4S):e689. Supplement, Sunday, May 5, 2019. Meeting Abstract: Using urine samples, the accuracy of C&S versus qPCR + NGS was compared in a 69 UTI patients in a prospective, feasibility, bi-institutional study. C&S failed to identify microbes in 17 infected patients. When compared, NGS test results were more accurate than C&S (97% versus 46%) and revealed a greater presence of polymicrobial pathogens. Read Abstract…