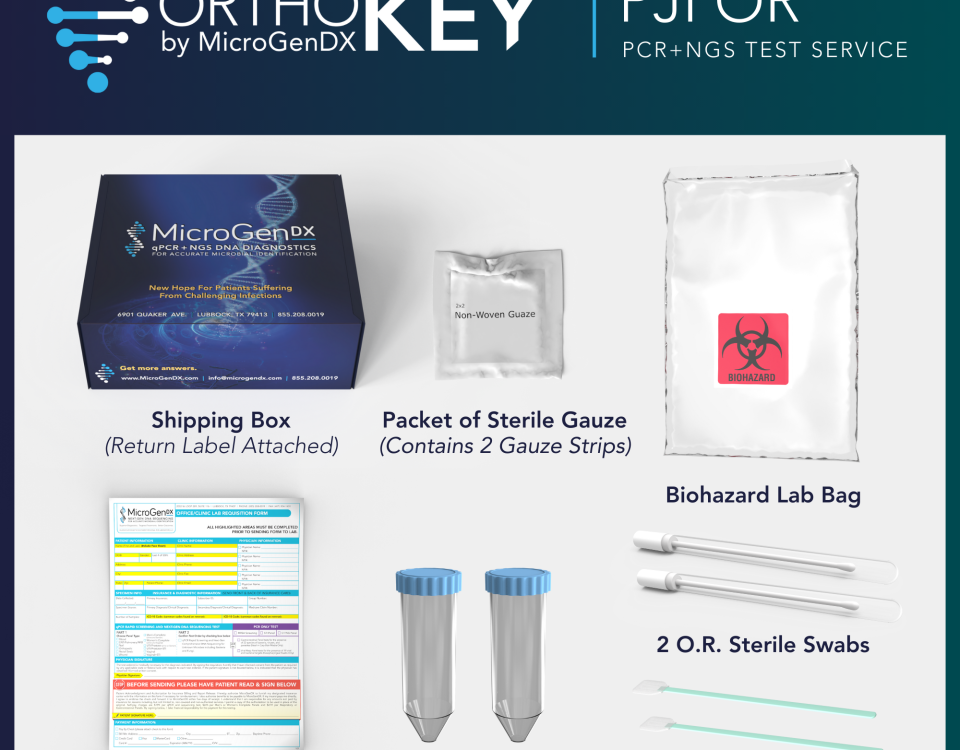
51 results found for: Periprosthetic joint infection
Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine Vol. 11, pages428–438(2018) Study: Despite significant progress in recent years, the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) remains a challenge and no gold standard test exists. A combination of serological, synovial, microbiological, histological, and radiological investigations is performed that are expensive, often invasive, and imperfect. Novel biomarkers and molecular methods have shown promise in recent years. The purpose of this review is to provide an update about the diagnostic recommendations for PJI and cover a selection of emerging diagnostic tools Read Study…
The Bone & Joint Journal 2018 Feb;100-B(2):127-133 Prospective Study:The diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection can be difficult due to the high rate of culturenegative infections. The aim of this study was to assess the use of next-generation sequencing for detecting organisms in synovial fluid. In this prospective, single-blinded study, 86 anonymized samples of synovial fluid were obtained from patients undergoing aspiration of the hip or knee as part of the investigation of a periprosthetic infection. A panel of synovial fluid tests, including levels of C-reactive protein, human neutrophil elastase, total neutrophil count, alpha-defensin, and culture were performed prior to next-generation […]
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) can be used to diagnose infectious diseases more rapidly and more accurately than traditional methods such as cultures, gram staining, and other biochemical and molecular tests that are organism-specific. In one reported case, NGS correctly identified the infectious organism after nearly 40 different diagnostic tests on 10 sample types. In another scenario, in cases of sepsis, timely targeted treatment with rapid identification of the microbial pathogen can be lifesaving. Instead of delaying diagnosis by ordering and waiting for organism-specific microbiology identification and susceptibility results, MicroGenDX’s qPCR+NGS can identify the bacterial, viral, or fungal source of infection and […]